what is a spectrometer|difference between spectroscopy and spectrometry : agency What is a Spectrometer? Formally speaking, a spectrometer is a scientific device that can separate a certain physical property (such as wavelength or mass) into individual spectra or ranges and measure them. WEB21 de ago. de 2023 · Our Mission. Mission Statement, Vision Statement, Ethos and Core Values. U.S. Customs and Border Protection Strategy 2021-2026. Performance, Accountability and Financial Reports.
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB7 de out. de 2023 · Em compromisso válido pela 26ª rodada do Campeonato Brasileiro, o Fortaleza recebe o América-MG neste domingo, às 18h30 (de Brasília). O duelo .
A spectrometer is an instrument that measures the variation of a physical characteristic over a range, such as light wavelength. Learn about the commo.
A spectrometer measures the wavelength and frequency of light, and allows us to identify and analyse the atoms in a sample we place . A spectrometer is an instrument that analyzes a range of a given characteristic for a substance, such as wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation. Learn about the sources, selection, and detection .What is a Spectrometer? Formally speaking, a spectrometer is a scientific device that can separate a certain physical property (such as wavelength or mass) into individual spectra or ranges and measure them.A spectrometer consists of several components A USB spectrometer is the most common type of spectrometer. They take light, separate it by wavelength and create a spectrum which shows the relative intensity of these separate .
mass spectrometry, analytic technique by which chemical substances are identified by the sorting of gaseous ions in electric and magnetic fields according to their mass-to-charge ratios. The instruments used in such .A spectrometer is any instrument used to probe a property of light as a function of its portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically its wavelength, frequency, or energy. The property being measured is usually intensity of light, but other variables like polarization can also be measured. Technically, a spectrometer can function over any range of light, but most operate in a .
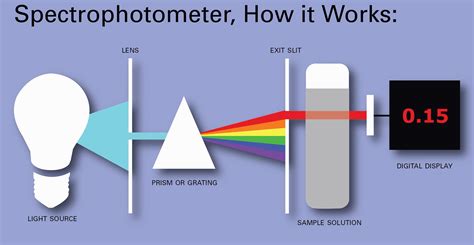
what does a spectrophotometer do
A spectrometer is a widely-used scientific tool for many disciplines, including biology, chemistry, agriculture and more. There are several kinds of spectrometers, each type with far-reaching applications and unique strengths. Mass spectrometers measure the mass-to-charge ratio and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectrometers measure nuclear .Grating spectrometer schematic Internal structure of a grating spectrometer: Light comes from left side and diffracts on the upper middle reflective grating. The wavelength of light is then selected by the slit on the upper right corner. An optical spectrometer (spectrophotometer, spectrograph or spectroscope) is an instrument used to measure properties of light over a . A spectrograph — sometimes called a spectroscope or spectrometer — breaks the light from a single material into its component colors the way a prism splits white light into a rainbow. It records this spectrum, which allows scientists to analyze the light and discover properties of the material interacting with it. Spectroscopy is as crucial .
An example of particle spectroscopy is a surface analysis technique known as electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS) that measures the energy lost when low-energy electrons (typically 5–10 electron volts) collide with a surface.Occasionally, the colliding electron loses energy by exciting the surface; by measuring the electron’s energy loss, vibrational excitations .What is an Optical Spectrometer? The core of any optical spectrometer is a component that separates light by wavelength. Most commonly this component is a diffraction grating – a sheet of material etched with repeating grooves that causes light reflected from it or transmitted through it to diffract and bend at an angle proportional to its wavelength. The spectrometer is an instrument that is used to measure and study the properties of light. It is also called a spectrograph or spectroscope.It is used to identify materials by studying the light emitted from or reflected from the materials. The spectrometer was invented by the German optical scientist Joseph Von Fraunhofer in 1814. Those spectrometers used a . A spectrometer is a scientific instrument used to separate and measure spectral components of a physical phenomenon (figure 1). The spectrometer is a broad term often used to describe instruments that measure a continuous variable of a phenomenon where the spectral components are somehow mixed.
A spectrometer is a device that allows scientists to dissect light into its constituent colors, akin to separating the vibrant hues of a rainbow. By precisely dispersing the light, spectrometers provide a unique window into the physical and chemical properties of objects.
A spectrometer is an aspect of the most responsible spectrophotometer for the calculation of different objects. A spectrophotometer is a comprehensive device that involves a light source, a way of collecting the light that has interacted with the objects being measured, and a measurement spectrometer.In 1955-56, Dow Chemical scientists Fred McLafferty and Roland Gohlke first demonstrated the combination of gas chromatography (GC) and mass spectrometry (MS) to identify individual substances in a mixture. This was the first coupling of a separation technology with a spectrometry technique to provide rapid characterization of chemical components. Mass spectrometry (MS) is a powerful qualitative and quantitative analytical technique used to identify and quantify a wide range of clinically relevant analytes.[1] When coupled with gas or liquid chromatographs, mass spectrometers allow the expansion of analytical capabilities to various clinical applications.[2] In addition, because of its ability to identify and .A spectrometer does something similar to what a prism does: light goes in, and gets split up into a spectrum. If you shine white light through a prism, a rainbow comes out the other side. But not all things give off white light. In fact, each element, when excited gives off a unique set of wavelengths that act like its signature: these are .
Eventually, the signal is transferred to a computer in which Fourier transform is carried out. Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\) is a block diagram of an FTIR spectrometer. Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\). Block diagram of an FTIR .spectrometer, leave these items in an alternate location. The magnetic field can also influence cardiac pacemakers and other medical devices. Discuss any such devices with your instructor and take the necessary precautions.
Key Takeaways: Mass Spectrometry. Fundamentals: Mass spectrometry quantifies the mass-to-charge ratio of molecules in a sample, aiding in substance quantification, compound identification, and structural elucidation.; Principles: Mass spectrometry operates by ionizing compounds, separating ions based on their mass-to-charge ratio, and detecting them .Mass spectrometry is an analytical tool useful for measuring the mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) of one or more molecules present in a sample. These measurements can often be used to calculate the exact molecular weight of the sample components as well. Typically, mass spectrometers can be used to identify unknown compounds via molecular weight determination, to quantify known . The sample absorbs some of the radiation, and the rest passes through the spectrometer to a detector. Radiation sources can be separated into two broad categories: line sources and continuum sources. Line sources excite the analyte and thus emit its own line spectrum. Hollow cathode lamps and electrodeless discharge lamps are the most commonly .Mass spectrometry has been described as the smallest scale in the world, not because of the mass spectrometer's size but because of the size of what it weighs -- molecules. Over the past decade, mass spectrometry has undergone tremendous technological improvements allowing for its application to proteins, peptides, carbohydrates, DNA, drugs .
Spectrometer modules can be paired with numerous accessories and mounted on a custom breadboard to power your project. Modular Spectrometers . Discover-It-Yourself Systems. The Discover-It-Yourself series from Metrohm Spectro is designed to help develop a new applications. These flexible systems can be customized for your requirements.
Spectrometer Optical Paths. The function of the optical components of the spectrometer is to image the entrance slit onto the detector or detector array. The spatial transmission of the light directed through the spectrometer by optical components is called the optical path. There are many path configurations in laboratory and field . Spectrophotometer Geometry. Spectrophotometer geometry defines the arrangement of the light source, the sample plane, and the detector. Choosing the correct geometry depends on your intended application:
A spectrometer can separate the component colors coming either directly from an emission source or from the light transmitted through a sample. A top-down diagram of a spectrometer is shown in Figure 2. Figure 2: The light path through a simple spectrometer.Spectroscopy is a branch of science concerned with the spectra of electromagnetic radiation as a function of its wavelength or frequency measured by spectrographic equipment, and other techniques, in order to obtain information concerning the structure and properties of matter. [4] Spectral measurement devices are referred to as spectrometers, spectrophotometers, .
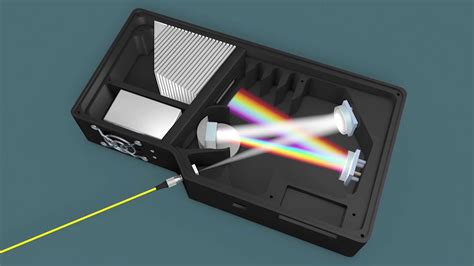
what does a spectrometer do
Riqueza Slots. Super jackpot | Cassino Online | Jogos de caça-níqueis on-line | Troca de criptografia para real | Jogo Aviador | Tigre da Fortuna | Boi da Fortuna | Coelho da Fortuna | Venha tentar a sorte!👇👇👇.
what is a spectrometer|difference between spectroscopy and spectrometry